Auto-heal unhealthy kubernetes pods
Kubernetes pods can become unhealthy due to various issues like resource constraints, configuration problems, or application failures. Manual intervention to diagnose and fix unhealthy pods creates operational overhead and delays in service recovery.
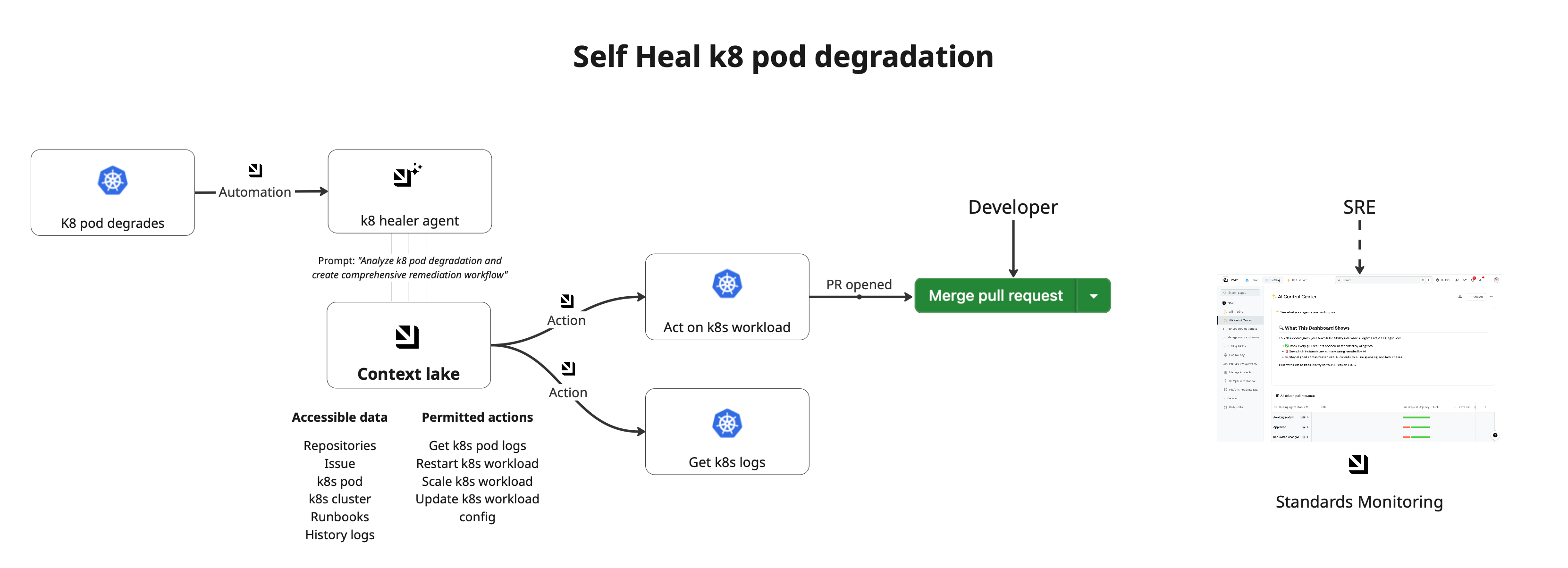
This guide demonstrates how to create an AI-powered system that automatically detects unhealthy pods, analyzes their logs and SDLC context, and triggers targeted remediation actions to restore service health.
The AI agent follows a guided process to first retrieve pod logs, combine them with SDLC context, intelligently determine the root cause, and execute targeted fixes like restarts, scaling, or configuration updates.
Common use cases
- Automatically restart pods that are in CrashLoopBackOff state due to application errors.
- Scale up resources when pods are failing due to memory limits or CPU constraints.
- Apply configuration fixes for common pod health issues like missing environment variables or incorrect resource requests.
- Trigger rollback procedures when pods fail after recent deployments.
- Notify teams about critical pod health issues requiring immediate attention.
Prerequisites
This guide assumes the following:
- You have a Port account and have completed the onboarding process.
- Port's Kubernetes integration is configured in your account.
- You have access to create and configure AI agents in Port.
- You have a Kubernetes cluster with pods that can be monitored and managed.
Set up self-service actions
We will create self-service actions that the AI agent can use for pod remediation.
Get kubernetes pod logs action
-
Go to the self-service page of your portal.
-
Click on
+ New Action. -
Click on the
{...} Edit JSONbutton. -
Copy and paste the following JSON configuration:
Get kubernetes pod logs action (Click to expand)
{
"identifier": "get_k8s_pod_logs",
"title": "Get Kubernetes Pod Logs",
"icon": "Cluster",
"description": "Stream logs from a Kubernetes pod to help with debugging and monitoring",
"trigger": {
"type": "self-service",
"operation": "DAY-2",
"userInputs": {
"properties": {
"container": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Container Name (optional)",
"description": "Specify container name if pod has multiple containers. Leave empty for default container."
},
"tail": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Number of Lines to Tail",
"description": "Number of recent log lines to retrieve (default: 200)",
"default": "200"
},
"follow": {
"type": "boolean",
"title": "Follow Logs",
"description": "Stream logs in real-time (like tail -f)",
"default": false
},
"since": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Since Time (optional)",
"description": "Only return logs newer than a relative duration like 5s, 2m, or 3h"
}
},
"required": []
},
"blueprintIdentifier": "k8s_pod"
},
"invocationMethod": {
"type": "GITHUB",
"org": "<YOUR-GITHUB-ORG>",
"repo": "<YOUR-GITHUB-REPO>",
"workflow": "get-pod-logs.yaml",
"workflowInputs": {
"port_context": {
"entity": "{{ .entity }}",
"runId": "{{ .run.id }}"
},
"inputs": "{{ .inputs }}"
},
"reportWorkflowStatus": true
},
"requiredApproval": false
} -
Click
Saveto create the action.
Restart kubernetes workload action
-
Go to the self-service page of your portal.
-
Click on
+ New Action. -
Click on the
{...} Edit JSONbutton. -
Copy and paste the following JSON configuration:
Restart kubernetes workload action (Click to expand)
{
"identifier": "restart_k8s_workload",
"title": "Restart Kubernetes Workload",
"icon": "Cluster",
"description": "Restart a Kubernetes workload (Deployment, StatefulSet, or DaemonSet) to resolve transient issues",
"trigger": {
"type": "self-service",
"operation": "DAY-2",
"userInputs": {
"properties": {
"reason": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Reason for Restart",
"description": "Brief explanation of why this workload needs to be restarted",
"default": "Healing unhealthy workload"
}
},
"required": []
},
"blueprintIdentifier": "k8s_workload"
},
"invocationMethod": {
"type": "GITHUB",
"org": "<YOUR-GITHUB-ORG>",
"repo": "<YOUR-GITHUB-REPO>",
"workflow": "restart-k8s-workload.yaml",
"workflowInputs": {
"port_context": {
"entity": "{{ .entity }}",
"runId": "{{ .run.id }}"
}
},
"reportWorkflowStatus": true
},
"requiredApproval": false
} -
Click
Saveto create the action.
Scale up kubernetes workload action
-
Go to the self-service page of your portal.
-
Click on
+ New Action. -
Click on the
{...} Edit JSONbutton. -
Copy and paste the following JSON configuration:
Scale up kubernetes workload action (Click to expand)
{
"identifier": "scale_k8s_workload",
"title": "Scale Kubernetes Workload",
"icon": "Cluster",
"description": "Scale a Kubernetes workload up or down to resolve resource issues",
"trigger": {
"type": "self-service",
"operation": "DAY-2",
"userInputs": {
"properties": {
"desired_replicas": {
"type": "number",
"title": "Desired Replicas",
"description": "Number of replicas to scale to",
"default": 3,
"minimum": 1,
"maximum": 20
},
"reason": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Reason for Scaling",
"description": "Brief explanation of why this workload needs to be scaled",
"default": "Scaling to resolve resource constraints"
}
},
"required": [
"desired_replicas"
]
},
"blueprintIdentifier": "k8s_workload"
},
"invocationMethod": {
"type": "GITHUB",
"org": "<YOUR-GITHUB-ORG>",
"repo": "<YOUR-GITHUB-REPO>",
"workflow": "scale-k8s-workload.yaml",
"workflowInputs": {
"desired_replicas": "{{ .inputs.\"desired_replicas\" }}",
"port_context": {
"entity": "{{ .entity }}",
"runId": "{{ .run.id }}"
}
},
"reportWorkflowStatus": true
},
"requiredApproval": false
} -
Click
Saveto create the action.
Update kubernetes config action
-
Go to the self-service page of your portal.
-
Click on
+ New Action. -
Click on the
{...} Edit JSONbutton. -
Copy and paste the following JSON configuration:
Update kubernetes config action (Click to expand)
{
"identifier": "update_k8s_workload_config",
"title": "Update Kubernetes Workload Configuration",
"icon": "Cluster",
"description": "Update resource limits and requests for a Kubernetes workload",
"trigger": {
"type": "self-service",
"operation": "DAY-2",
"userInputs": {
"properties": {
"memory_limit": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Memory Limit",
"description": "Memory limit (e.g., 512Mi, 1Gi)",
"default": "512Mi",
"pattern": "^[0-9]+(Mi|Gi)$"
},
"cpu_limit": {
"type": "string",
"title": "CPU Limit",
"description": "CPU limit (e.g., 500m, 1)",
"default": "500m",
"pattern": "^[0-9]+(m|)$"
},
"memory_request": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Memory Request",
"description": "Memory request (e.g., 256Mi, 512Mi)",
"default": "256Mi",
"pattern": "^[0-9]+(Mi|Gi)$"
},
"cpu_request": {
"type": "string",
"title": "CPU Request",
"description": "CPU request (e.g., 250m, 500m)",
"default": "250m",
"pattern": "^[0-9]+(m|)$"
},
"reason": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Reason for Update",
"description": "Brief explanation of why this configuration needs to be updated",
"default": "Updating resource configuration to resolve health issues"
}
},
"required": [
"memory_limit",
"cpu_limit",
"memory_request",
"cpu_request"
]
},
"blueprintIdentifier": "k8s_workload"
},
"invocationMethod": {
"type": "GITHUB",
"org": "<YOUR-GITHUB-ORG>",
"repo": "<YOUR-GITHUB-REPO>",
"workflow": "update-k8s-workload-config.yaml",
"workflowInputs": {
"port_context": {
"entity": "{{ .entity }}",
"runId": "{{ .run.id }}"
}
},
"reportWorkflowStatus": true
},
"requiredApproval": false
} -
Click
Saveto create the action.
Set up GitHub workflows
We will create GitHub workflows to be triggered by the self-service actions.
We recommend creating a dedicated repository for the workflows that are used by Port actions.
Add GitHub secrets
In your GitHub repository, go to Settings > Secrets and add the following secrets:
PORT_CLIENT_ID- Your portclient idHow to get the credentials.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET- Your portclient secretHow to get the credentials.KUBECONFIG- Your kubeconfig file encoded in base64.
Get kubernets logs GitHub workflow
-
Create the file
.github/workflows/get-k8s-pod-logs.yamlin the.github/workflowsfolder of your repository. -
Copy and paste the following content:
Get kubernetes logs GitHub workflow (Click to expand)
name: Get Kubernetes Pod Logs
on:
workflow_dispatch:
inputs:
port_context:
required: true
type: string
description: "Port context containing entity and runId"
inputs:
required: false
type: string
description: "User inputs for the action"
jobs:
pod-logs:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout repository
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Parse Port context
id: parse-context
run: |
# Debug: Show the raw input
echo "Raw port_context input:"
echo '${{ inputs.port_context }}'
echo ""
# Parse with error handling
RUN_ID=$(echo '${{ inputs.port_context }}' | jq -r '.runId // empty')
ENTITY=$(echo '${{ inputs.port_context }}' | jq -r '.entity // empty')
POD_IDENTIFIER=$(echo '${{ inputs.port_context }}' | jq -r '.entity.identifier // empty')
POD_TITLE=$(echo '${{ inputs.port_context }}' | jq -r '.entity.title // empty')
# Handle Pod Name - extract real pod name from Port identifier
# Port identifier format: "pod-name-namespace-cluster" (e.g., "api-backend-7bd58f9457-dhblj-production-minikube-cluster")
# Real pod name format: "pod-name" (e.g., "api-backend-7bd58f9457-dhblj")
if [[ "$POD_IDENTIFIER" =~ ^(.+)-[^-]+-minikube-cluster$ ]]; then
POD_NAME="${BASH_REMATCH[1]}"
echo "🔍 Extracted real pod name from Port identifier: $POD_NAME"
else
POD_NAME="$POD_IDENTIFIER"
echo "📍 Using identifier as pod name: $POD_NAME"
fi
# Handle namespace - get from Port entity properties
NAMESPACE=$(echo '${{ inputs.port_context }}' | jq -r '.entity.properties.namespace // empty' 2>/dev/null)
if [ -z "$NAMESPACE" ] || [ "$NAMESPACE" = "null" ]; then
echo "⚠️ Namespace not found in entity properties, defaulting to production"
NAMESPACE="production"
fi
echo "📍 Using namespace: $NAMESPACE"
# Handle cluster - try multiple sources
CLUSTER=$(echo '${{ inputs.port_context }}' | jq -r '.entity.properties.cluster // empty' 2>/dev/null)
if [ -z "$CLUSTER" ] || [ "$CLUSTER" = "null" ]; then
# Try to extract from pod name or use default
CLUSTER="default-cluster"
echo "⚠️ Cluster not found in entity properties, using default-cluster"
fi
# Validate required fields
if [ -z "$RUN_ID" ] || [ -z "$POD_NAME" ]; then
echo "❌ Error: Missing required fields in port_context"
echo "RUN_ID: $RUN_ID"
echo "POD_NAME: $POD_NAME"
exit 1
fi
# Set outputs with proper escaping
{
echo "runId<<EOF"
echo "$RUN_ID"
echo "EOF"
} >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
{
echo "entity<<EOF"
echo "$ENTITY"
echo "EOF"
} >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
{
echo "podName<<EOF"
echo "$POD_NAME"
echo "EOF"
} >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
{
echo "podTitle<<EOF"
echo "$POD_TITLE"
echo "EOF"
} >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
{
echo "namespace<<EOF"
echo "$NAMESPACE"
echo "EOF"
} >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
{
echo "cluster<<EOF"
echo "$CLUSTER"
echo "EOF"
} >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
# Debug: Show parsed values
echo "Parsed values:"
echo "RUN_ID: $RUN_ID"
echo "POD_IDENTIFIER: $POD_IDENTIFIER"
echo "POD_NAME: $POD_NAME"
echo "POD_TITLE: $POD_TITLE"
echo "NAMESPACE: $NAMESPACE"
echo "CLUSTER: $CLUSTER"
- name: Parse user inputs
id: parse-inputs
run: |
# Debug: Show the raw inputs
echo "Raw inputs:"
echo '${{ inputs.inputs }}'
echo ""
if [ -n "${{ inputs.inputs }}" ] && [ "${{ inputs.inputs }}" != "null" ]; then
# Parse with error handling
CONTAINER=$(echo '${{ inputs.inputs }}' | jq -r '.container // empty' 2>/dev/null || echo "")
TAIL=$(echo '${{ inputs.inputs }}' | jq -r '.tail // "200"' 2>/dev/null || echo "200")
FOLLOW=$(echo '${{ inputs.inputs }}' | jq -r '.follow // false' 2>/dev/null || echo "false")
SINCE=$(echo '${{ inputs.inputs }}' | jq -r '.since // empty' 2>/dev/null || echo "")
{
echo "container<<EOF"
echo "$CONTAINER"
echo "EOF"
} >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
{
echo "tail<<EOF"
echo "$TAIL"
echo "EOF"
} >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
{
echo "follow<<EOF"
echo "$FOLLOW"
echo "EOF"
} >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
{
echo "since<<EOF"
echo "$SINCE"
echo "EOF"
} >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
else
{
echo "container<<EOF"
echo ""
echo "EOF"
} >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
{
echo "tail<<EOF"
echo "200"
echo "EOF"
} >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
{
echo "follow<<EOF"
echo "false"
echo "EOF"
} >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
{
echo "since<<EOF"
echo ""
echo "EOF"
} >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
fi
# Debug: Show parsed input values
echo "Parsed input values:"
echo "CONTAINER: $CONTAINER"
echo "TAIL: $TAIL"
echo "FOLLOW: $FOLLOW"
echo "SINCE: $SINCE"
- name: Inform Port of workflow start
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{ steps.parse-context.outputs.runId }}
logMessage: "🚀 Starting pod logs retrieval for ${{ steps.parse-context.outputs.podTitle }} in namespace ${{ steps.parse-context.outputs.namespace }} on cluster ${{ steps.parse-context.outputs.cluster }}..."
- name: Setup kubectl
uses: azure/setup-kubectl@v3
with:
version: 'latest'
- name: Configure kubeconfig
run: |
# Create .kube directory
mkdir -p ~/.kube
# Check if KUBECONFIG secret is provided
if [ -n "${{ secrets.KUBECONFIG }}" ]; then
echo "🔧 Using kubeconfig from GitHub secret..."
echo "${{ secrets.KUBECONFIG }}" | base64 -d > ~/.kube/config
chmod 600 ~/.kube/config
echo "✅ Kubeconfig configured from secret"
else
echo "❌ No KUBECONFIG secret found!"
echo "Please add your kubeconfig as a GitHub secret named 'KUBECONFIG'"
echo "You can generate it by running: cat ~/.kube/config | base64 -w 0"
exit 1
fi
# Display current context
echo "📍 Current kubectl context:"
kubectl config current-context || echo "No context set"
# Show available contexts
echo "📋 Available contexts:"
kubectl config get-contexts || echo "No contexts available"
- name: Verify kubectl access
run: |
echo "🔍 Verifying kubectl access..."
echo "📍 Cluster info:"
kubectl cluster-info --request-timeout=10s --insecure-skip-tls-verify || echo "⚠️ Could not get cluster info"
echo ""
echo "📋 Available pods in namespace ${{ steps.parse-context.outputs.namespace }}:"
kubectl get pods -n ${{ steps.parse-context.outputs.namespace }} --no-headers --insecure-skip-tls-verify | head -5 || echo "❌ No pods found or access denied"
echo "✅ kubectl access verified"
- name: Check if pod exists
id: check-pod
run: |
if kubectl get pod ${{ steps.parse-context.outputs.podName }} -n ${{ steps.parse-context.outputs.namespace }} --insecure-skip-tls-verify >/dev/null 2>&1; then
echo "exists=true" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
echo "✅ Pod ${{ steps.parse-context.outputs.podName }} found in namespace ${{ steps.parse-context.outputs.namespace }}"
else
echo "exists=false" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
echo "❌ Pod ${{ steps.parse-context.outputs.podName }} not found in namespace ${{ steps.parse-context.outputs.namespace }}"
fi
- name: Get pod information
if: steps.check-pod.outputs.exists == 'true'
run: |
echo "📋 Pod Information:"
kubectl describe pod ${{ steps.parse-context.outputs.podName }} -n ${{ steps.parse-context.outputs.namespace }} --insecure-skip-tls-verify | head -20
- name: Stream pod logs to Port
if: steps.check-pod.outputs.exists == 'true'
shell: bash
run: |
RUN_ID="${{ steps.parse-context.outputs.runId }}"
POD_NAME="${{ steps.parse-context.outputs.podName }}"
NAMESPACE="${{ steps.parse-context.outputs.namespace }}"
CONTAINER="${{ steps.parse-inputs.outputs.container }}"
TAIL="${{ steps.parse-inputs.outputs.tail }}"
FOLLOW="${{ steps.parse-inputs.outputs.follow }}"
SINCE="${{ steps.parse-inputs.outputs.since }}"
# Build kubectl logs command
KUBECTL_CMD="kubectl logs $POD_NAME -n $NAMESPACE --insecure-skip-tls-verify"
if [ -n "$CONTAINER" ]; then
KUBECTL_CMD="$KUBECTL_CMD -c $CONTAINER"
fi
if [ -n "$TAIL" ]; then
KUBECTL_CMD="$KUBECTL_CMD --tail=$TAIL"
fi
if [ -n "$SINCE" ]; then
KUBECTL_CMD="$KUBECTL_CMD --since=$SINCE"
fi
echo "🔍 Executing: $KUBECTL_CMD"
# Execute kubectl logs and capture output
set +e
echo "📄 Retrieving logs..."
LOG_OUTPUT=$($KUBECTL_CMD 2>&1)
LOG_STATUS=$?
set -e
# Save logs to file for the summary
if [ $LOG_STATUS -eq 0 ]; then
echo "SUCCESS" > status.txt
echo "✅ Logs retrieved successfully"
# Save logs to file (truncate if too long)
echo "$LOG_OUTPUT" | head -100 > pod_logs.txt
echo "📊 Retrieved $(echo "$LOG_OUTPUT" | wc -l) lines of logs"
else
echo "FAILURE" > status.txt
echo "❌ Failed to retrieve logs (exit code: $LOG_STATUS)"
echo "Error: $LOG_OUTPUT" > pod_logs.txt
fi
- name: Handle pod not found
if: steps.check-pod.outputs.exists == 'false'
run: |
echo "❌ Pod not found - cannot retrieve logs"
echo "FAILURE" > status.txt
echo "Pod not found in namespace ${{ steps.parse-context.outputs.namespace }}" > pod_logs.txt
- name: Prepare summary with logs
if: always()
id: prepare-summary
run: |
if [ -f pod_logs.txt ]; then
LOGS_CONTENT=$(cat pod_logs.txt)
# Create summary with logs
SUMMARY="## 📋 Pod Logs for ${{ steps.parse-context.outputs.podName }}
**Namespace:** ${{ steps.parse-context.outputs.namespace }}
**Status:** $(cat status.txt 2>/dev/null || echo 'UNKNOWN')
### 📄 Logs:
\`\`\`
$LOGS_CONTENT
\`\`\`"
else
SUMMARY="Failed to retrieve logs for pod ${{ steps.parse-context.outputs.podName }}"
fi
# Save summary to output (escape for GitHub Actions)
{
echo "summary<<EOF"
echo "$SUMMARY"
echo "EOF"
} >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
- name: Inform Port about result
if: always()
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{ steps.parse-context.outputs.runId }}
status: ${{ steps.check-pod.outputs.exists == 'true' && 'SUCCESS' || 'FAILURE' }}
logMessage: ${{ steps.check-pod.outputs.exists == 'true' && '✅ Pod logs retrieval completed successfully!' || '❌ Pod logs retrieval failed - pod not found' }}
summary: ${{ steps.prepare-summary.outputs.summary }}
Restart kubernetes workload GitHub workflow
-
Create the file
.github/workflows/restart-k8s-workload.yamlin the.github/workflowsfolder of your repository. -
Copy and paste the following content:
Restart kubernetes workload GitHub workflow (Click to expand)
name: Restart Kubernetes Workload
on:
workflow_dispatch:
inputs:
port_context:
required: true
description: 'Action and general context (blueprint, entity, run id, etc...)'
type: string
jobs:
restart-workload:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: 'actions/checkout@v4'
- name: Inform Port of workflow start
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId}}
logMessage: Starting restart of Kubernetes workload ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }}
- name: Configure kubectl
run: |
# NOTE: In production, this should connect to your production cluster with proper SSL verification
# For this demo, we're using a local cluster through ngrok tunnel, so we skip TLS verification
echo "🔧 Using kubeconfig from GitHub secret..."
echo "${{ secrets.KUBECONFIG }}" | base64 -d > kubeconfig.yaml
export KUBECONFIG=kubeconfig.yaml
echo "✅ Kubeconfig configured from secret"
echo "📍 Current kubectl context:"
kubectl config current-context --insecure-skip-tls-verify
echo "📋 Available contexts:"
kubectl config get-contexts
echo "🔍 Verifying kubectl access..."
kubectl cluster-info --request-timeout=10s --insecure-skip-tls-verify
echo "✅ kubectl access verified"
- name: Restart Kubernetes workload
run: |
export KUBECONFIG=kubeconfig.yaml
WORKLOAD_NAME="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }}"
NAMESPACE="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.properties.namespace }}"
WORKLOAD_TYPE="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.properties.kind }}"
echo "Restarting $WORKLOAD_TYPE: $WORKLOAD_NAME in namespace: $NAMESPACE"
case $WORKLOAD_TYPE in
"Deployment")
kubectl rollout restart deployment/$WORKLOAD_NAME -n $NAMESPACE --insecure-skip-tls-verify
kubectl rollout status deployment/$WORKLOAD_NAME -n $NAMESPACE --timeout=300s --insecure-skip-tls-verify
;;
"StatefulSet")
kubectl rollout restart statefulset/$WORKLOAD_NAME -n $NAMESPACE --insecure-skip-tls-verify
kubectl rollout status statefulset/$WORKLOAD_NAME -n $NAMESPACE --timeout=300s --insecure-skip-tls-verify
;;
"DaemonSet")
kubectl rollout restart daemonset/$WORKLOAD_NAME -n $NAMESPACE --insecure-skip-tls-verify
kubectl rollout status daemonset/$WORKLOAD_NAME -n $NAMESPACE --timeout=300s --insecure-skip-tls-verify
;;
*)
echo "Unsupported workload type: $WORKLOAD_TYPE"
exit 1
;;
esac
- name: Verify workload health
run: |
export KUBECONFIG=kubeconfig.yaml
WORKLOAD_NAME="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }}"
NAMESPACE="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.properties.namespace }}"
WORKLOAD_TYPE="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.properties.kind }}"
echo "Checking health of $WORKLOAD_TYPE: $WORKLOAD_NAME"
kubectl get $WORKLOAD_TYPE $WORKLOAD_NAME -n $NAMESPACE --insecure-skip-tls-verify
kubectl get pods -l app=$WORKLOAD_NAME -n $NAMESPACE --insecure-skip-tls-verify
- name: Inform Port about restart success
if: success()
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId }}
status: 'SUCCESS'
logMessage: ✅ Successfully restarted Kubernetes workload ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }}
summary: Kubernetes workload restart completed successfully
- name: Inform Port about restart failure
if: failure()
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId }}
status: 'FAILURE'
logMessage: ❌ Failed to restart Kubernetes workload ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }}
summary: Kubernetes workload restart failed
Scale up kubernetes workload GitHub workflow
-
Create the file
.github/workflows/scale-k8s-workload.yamlin the.github/workflowsfolder of your repository. -
Copy and paste the following content:
Scale up kubernetes workload GitHub workflow (Click to expand)
name: Scale Kubernetes Workload
on:
workflow_dispatch:
inputs:
desired_replicas:
required: true
description: 'Number of replicas to scale to'
type: string
port_context:
required: true
description: 'Action and general context (blueprint, entity, run id, etc...)'
type: string
jobs:
scale-workload:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: 'actions/checkout@v4'
- name: Inform Port of workflow start
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId}}
logMessage: Starting scale operation for Kubernetes workload ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }}
- name: Configure kubectl
run: |
# NOTE: In production, this should connect to your production cluster with proper SSL verification
# For this demo, we're using a local cluster through ngrok tunnel, so we skip TLS verification
echo "🔧 Using kubeconfig from GitHub secret..."
echo "${{ secrets.KUBECONFIG }}" | base64 -d > kubeconfig.yaml
export KUBECONFIG=kubeconfig.yaml
echo "✅ Kubeconfig configured from secret"
echo "📍 Current kubectl context:"
kubectl config current-context --insecure-skip-tls-verify
echo "📋 Available contexts:"
kubectl config get-contexts
echo "🔍 Verifying kubectl access..."
kubectl cluster-info --request-timeout=10s --insecure-skip-tls-verify
echo "✅ kubectl access verified"
- name: Scale Kubernetes workload
run: |
export KUBECONFIG=kubeconfig.yaml
WORKLOAD_NAME="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }}"
NAMESPACE="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.properties.namespace }}"
WORKLOAD_TYPE="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.properties.kind }}"
REPLICAS="${{ inputs.desired_replicas }}"
echo "Scaling $WORKLOAD_TYPE: $WORKLOAD_NAME to $REPLICAS replicas in namespace: $NAMESPACE"
case $WORKLOAD_TYPE in
"Deployment")
kubectl --insecure-skip-tls-verify scale deployment/$WORKLOAD_NAME --replicas=$REPLICAS -n $NAMESPACE
kubectl --insecure-skip-tls-verify rollout status deployment/$WORKLOAD_NAME -n $NAMESPACE --timeout=300s
;;
"StatefulSet")
kubectl --insecure-skip-tls-verify scale statefulset/$WORKLOAD_NAME --replicas=$REPLICAS -n $NAMESPACE
kubectl --insecure-skip-tls-verify rollout status statefulset/$WORKLOAD_NAME -n $NAMESPACE --timeout=300s
;;
"ReplicaSet")
kubectl --insecure-skip-tls-verify scale replicaset/$WORKLOAD_NAME --replicas=$REPLICAS -n $NAMESPACE
;;
*)
echo "Unsupported workload type for scaling: $WORKLOAD_TYPE"
exit 1
;;
esac
- name: Verify scaling
run: |
export KUBECONFIG=kubeconfig.yaml
WORKLOAD_NAME="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }}"
NAMESPACE="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.properties.namespace }}"
WORKLOAD_TYPE="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.properties.kind }}"
echo "Checking scaled $WORKLOAD_TYPE: $WORKLOAD_NAME"
kubectl --insecure-skip-tls-verify get $WORKLOAD_TYPE $WORKLOAD_NAME -n $NAMESPACE
kubectl --insecure-skip-tls-verify get pods -l app=$WORKLOAD_NAME -n $NAMESPACE
- name: Inform Port about scaling success
if: success()
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId }}
status: 'SUCCESS'
logMessage: ✅ Successfully scaled Kubernetes workload ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }}
summary: Kubernetes workload scaling completed successfully
- name: Inform Port about scaling failure
if: failure()
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId }}
status: 'FAILURE'
logMessage: ❌ Failed to scale Kubernetes workload ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }}
summary: Kubernetes workload scaling failed
Update kubernetes config GitHub workflow
-
Create the file
.github/workflows/update-k8s-workload-config.yamlin the.github/workflowsfolder of your repository. -
Copy and paste the following content:
Update kubernetes config GitHub workflow (Click to expand)
name: Update Kubernetes Workload Configuration
on:
workflow_dispatch:
inputs:
port_context:
required: true
description: 'Action and general context (blueprint, entity, run id, etc...)'
type: string
jobs:
update-workload-config:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: 'actions/checkout@v4'
- name: Inform Port of workflow start
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId}}
logMessage: Starting configuration update for Kubernetes workload ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }}
- name: Configure kubectl for local cluster
run: |
echo "${{ secrets.KUBECONFIG }}" | base64 -d > kubeconfig.yaml
export KUBECONFIG=kubeconfig.yaml
kubectl config current-context
- name: Update workload configuration
run: |
WORKLOAD_NAME="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }}"
NAMESPACE="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.properties.namespace }}"
WORKLOAD_TYPE="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.properties.kind }}"
MEMORY_LIMIT="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.properties.memory_limit }}"
CPU_LIMIT="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.properties.cpu_limit }}"
MEMORY_REQUEST="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.properties.memory_request }}"
CPU_REQUEST="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.properties.cpu_request }}"
echo "Updating $WORKLOAD_TYPE: $WORKLOAD_NAME configuration in namespace: $NAMESPACE"
echo "Memory Limit: $MEMORY_LIMIT, CPU Limit: $CPU_LIMIT"
echo "Memory Request: $MEMORY_REQUEST, CPU Request: $CPU_REQUEST"
# Create a patch for resource limits and requests
cat > resource-patch.json << EOF
{
"spec": {
"template": {
"spec": {
"containers": [
{
"name": "$WORKLOAD_NAME",
"resources": {
"limits": {
"memory": "$MEMORY_LIMIT",
"cpu": "$CPU_LIMIT"
},
"requests": {
"memory": "$MEMORY_REQUEST",
"cpu": "$CPU_REQUEST"
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
}
EOF
case $WORKLOAD_TYPE in
"Deployment")
kubectl patch deployment $WORKLOAD_NAME -n $NAMESPACE --type='merge' -p "$(cat resource-patch.json)"
kubectl rollout status deployment/$WORKLOAD_NAME -n $NAMESPACE --timeout=300s
;;
"StatefulSet")
kubectl patch statefulset $WORKLOAD_NAME -n $NAMESPACE --type='merge' -p "$(cat resource-patch.json)"
kubectl rollout status statefulset/$WORKLOAD_NAME -n $NAMESPACE --timeout=300s
;;
"DaemonSet")
kubectl patch daemonset $WORKLOAD_NAME -n $NAMESPACE --type='merge' -p "$(cat resource-patch.json)"
kubectl rollout status daemonset/$WORKLOAD_NAME -n $NAMESPACE --timeout=300s
;;
*)
echo "Unsupported workload type for configuration update: $WORKLOAD_TYPE"
exit 1
;;
esac
- name: Verify configuration update
run: |
WORKLOAD_NAME="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }}"
NAMESPACE="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.properties.namespace }}"
WORKLOAD_TYPE="${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.properties.kind }}"
echo "Checking updated $WORKLOAD_TYPE: $WORKLOAD_NAME"
kubectl get $WORKLOAD_TYPE $WORKLOAD_NAME -n $NAMESPACE
kubectl describe $WORKLOAD_TYPE $WORKLOAD_NAME -n $NAMESPACE | grep -A 10 "Resources:"
- name: Inform Port about config update success
if: success()
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId }}
status: 'SUCCESS'
logMessage: ✅ Successfully updated Kubernetes workload configuration ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }}
summary: Kubernetes workload configuration update completed successfully
- name: Inform Port about config update failure
if: failure()
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId }}
status: 'FAILURE'
logMessage: ❌ Failed to update Kubernetes workload configuration ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }}
summary: Kubernetes workload configuration update failed
Create k8s pod healing AI agent
Next, we will create an AI agent that analyzes pod health issues and creates comprehensive remediation workflows.
-
Go to the AI Agents page of your portal.
-
Click on
+ AI Agent. -
Toggle
Json modeon. -
Copy and paste the following JSON schema:
K8s Pod healing AI agent configuration (Click to expand)
{
"identifier": "k8s_healing_agent",
"title": "Kubernetes Healing Agent",
"icon": "Cluster",
"properties": {
"description": "AI agent specialized in diagnosing and automatically fixing unhealthy Kubernetes workloads. Monitors pod health, identifies root causes, and applies appropriate fixes.",
"status": "active",
"prompt": "You are a Kubernetes healing AI agent with access to comprehensive SDLC data and pod logs.\n\n**Your healing process:**\n1. **FIRST - Get Logs**: Always start by retrieving pod logs using the get_k8s_pod_logs action to understand what's actually happening\n2. **Analyze with Context**: Combine log data with SDLC information (recent deployments, code changes, configuration updates) to build a complete picture\n3. **Intelligent Diagnosis**: Based on logs and context, determine the root cause (crashes, resource constraints, configuration issues, etc.)\n4. **Targeted Fix**: Execute only the specific action that will resolve the issue:\n - Restart for crashes and transient issues\n - Scale for resource constraints (CPU/memory)\n - Update config for resource limit issues\n - Create PR for complex fixes requiring code changes\n5. **Explain Your Actions**: Always explain what you found in the logs and why you chose the specific fix in your response",
"execution_mode": "Automatic",
"conversation_starters": [
"Analyze this unhealthy workload and suggest fixes",
"This pod is in CrashLoopBackOff, what should I do?",
"Help me diagnose why this workload is failing",
"Scale up resources for this memory-constrained workload",
"What's causing this ImagePullBackOff error?",
"Why are my pods stuck in Pending state?"
],
"tools": [
"^(list|search|track|describe)_.*",
"run_get_k8s_pod_logs",
"run_restart_k8s_workload",
"run_scale_k8s_workload",
"run_update_k8s_workload_config",
"run_create_k8s_fix_pr"
]
},
"relations": {}
}MCP Enhanced CapabilitiesThe AI agent uses MCP (Model Context Protocol) enhanced capabilities to automatically discover important and relevant blueprint entities via its tools. The
^(list|search|track|describe)_.*pattern allows the agent to access and analyze related entities across your entire software catalog, including Kubernetes resources, recent deployments, code changes, runbooks, and history logs. This gives the agent rich SDLC context to make intelligent healing decisions. Additionally, we explicitly add the remediation action tools (run_get_k8s_pod_logs,run_restart_k8s_workload, etc.), which the agent calls sequentially to diagnose and fix unhealthy workloads. -
Click
Createto save the agent.
Set up automation
Next, we will create an automation to trigger the ai agent when the health of a Kubernetes pod moves from healthy to unhealthy.
Follow the steps below to create the automation:
-
Go to the automations page of your portal.
-
Click on
+ Automation. -
Copy and paste the following JSON schema:
Kubernetes workload healing automation (Click to expand)
{
"identifier": "k8s_workload_healing_automation",
"title": "Kubernetes Workload Healing Automation",
"description": "Automatically trigger AI healing agent when Kubernetes workloads become unhealthy",
"icon": "Cluster",
"trigger": {
"type": "automation",
"event": {
"type": "ENTITY_UPDATED",
"blueprintIdentifier": "k8s_workload"
},
"condition": {
"type": "JQ",
"expressions": [
".diff.before.properties.isHealthy == \"Healthy\"",
".diff.after.properties.isHealthy == \"Unhealthy\""
],
"combinator": "and"
}
},
"invocationMethod": {
"type": "WEBHOOK",
"url": "https://api.getport.io/v1/agent/k8s_healing_agent/invoke",
"agent": false,
"synchronized": true,
"method": "POST",
"headers": {
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
"body": {
"prompt": "Workload `{{ .event.diff.after.title }}` in namespace `{{ .event.diff.after.properties.namespace }}` is **UNHEALTHY**.\n\n**Current State**: {{ .event.diff.after.properties.replicas }} replicas, {{ .event.diff.after.properties.readyReplicas }} ready\n\n**Healing Process**:\n1. First, get the pod logs to understand what's happening\n2. Analyze the logs with SDLC context (recent deployments, code changes)\n3. Determine the root cause and appropriate fix\n4. Execute only the targeted action that will resolve the issue\n\nStart by retrieving logs and then proceed with the analysis and fix.",
"labels": {
"source": "Automation",
"workload_name": "{{ .event.diff.after.identifier }}",
"namespace": "{{ .event.diff.after.properties.namespace }}",
"trigger_type": "health_degradation"
}
}
},
"publish": true
} -
Click
Createto save the automation.
Let's test it
Now let us test the complete workflow to ensure everything works correctly.
- Go to your Kubernetes cluster and create a pod with an intentionally failing configuration (e.g., wrong image name, missing environment variables, or resource limits too low).
- Wait for the pod to enter an unhealthy state (CrashLoopBackOff, ImagePullBackOff, etc.).
- Verify that the pod appears in Port with the correct health status.
- Check the audit log to monitor the automation and the ai agent.
- Check your GitHub repository to monitor the workflow that has been triggered by the agent.
- Check the PR that has been created by the agent for the fix.
- Approve the PR to fix the issue and have pod healed.