Track AI adoption and impact
Tracking AI adoption provides visibility into how engineering teams are leveraging AI coding agents and the impact these tools have on delivery outcomes. Without visibility into AI usage patterns, teams struggle to understand adoption rates, measure productivity gains, and identify which teams or services benefit most from AI assistance.
This guide helps engineering managers, platform engineers, and product leaders answer critical questions about AI adoption:
- Adoption: Which teams and services are using AI coding tools?
- Impact: How does AI assistance affect PR throughput and cycle time?
- Effectiveness: Are AI-assisted PRs delivering faster or higher quality outcomes?
- Cost optimization: Are AI tool licenses being fully utilized?
By the end of this guide, you will have dashboards that track AI adoption metrics, enabling you to understand usage patterns, measure productivity impact, and make informed decisions about AI tool investments across your organization.
Common use cases
- Compare PR throughput and cycle time between AI-assisted and traditional workflows.
- Identify teams and services with the highest AI adoption rates.
- Track AI usage trends over time to understand adoption patterns.
- Monitor AI tool license utilization and revoke unused licenses to optimize costs.
- Correlate AI adoption with operational metrics like bug rates and incident resolution time.
Prerequisites
This guide assumes the following:
- You have a Port account and have completed the onboarding process.
- Port's GitHub integration is installed in your account.
- The
githubPullRequestandgithubRepositoryblueprints are already created (these are created when you install the GitHub integration). - For Cursor tracking: Port's Cursor integration is installed in your account.
- For Copilot tracking: Port's GitHub Copilot integration is installed in your account.
- For AI impact on operations: Port's Jira integration is installed in your account (optional, for tracking bugs, security issues, and incidents).
Set up data model
We will create and update blueprints to support AI adoption tracking.
Update the User blueprint
Depending on which AI tool you want to track, you need to update the User blueprint with the appropriate properties.
- Cursor
- GitHub Copilot
Ensure you have installed the Cursor integration before proceeding.
Add properties to track Cursor license and usage status.
-
Go to the Builder page of your portal.
-
Find the
Userblueprint and click on it. -
Click on the
{...}button in the top right corner, and chooseEdit JSON. -
Add the following properties to the
propertiessection:Cursor license properties for User blueprint (click to expand)
"cursor_licensed": {
"title": "Cursor Licensed",
"type": "boolean",
"description": "Whether the user has a Cursor license"
},
"cursor_active": {
"title": "Cursor Active",
"type": "boolean",
"description": "Whether the user has used Cursor in the last 90 days"
},
"cursor_last_active": {
"title": "Cursor Last Active",
"type": "string",
"format": "date-time",
"description": "Last time the user used Cursor"
} -
Click
Saveto update the blueprint.
Ensure you have installed the GitHub Copilot integration before proceeding.
Add properties to track Copilot license and usage status.
-
Go to the Builder page of your portal.
-
Find the
Userblueprint and click on it. -
Click on the
{...}button in the top right corner, and chooseEdit JSON. -
Add the following properties to the
propertiessection:Copilot license properties for User blueprint (click to expand)
"copilot_licensed": {
"title": "Copilot Licensed",
"type": "boolean",
"description": "Whether the user has a GitHub Copilot license"
},
"copilot_active": {
"title": "Copilot Active",
"type": "boolean",
"description": "Whether the user has used Copilot in the last 90 days"
},
"copilot_last_active": {
"title": "Copilot Last Active",
"type": "string",
"format": "date-time",
"description": "Last time the user used Copilot"
} -
Click
Saveto update the blueprint.
Update the pull request blueprint
Regardless of which AI tool you're tracking, you need to add a property to identify AI-assisted PRs.
-
Go to the Builder page of your portal.
-
Find the
githubPullRequestblueprint and click on it. -
Click on the
{...}button in the top right corner, and chooseEdit JSON. -
Add the following property to the
propertiessection:AI agent property for Pull Request blueprint (click to expand)
"created_by_agent": {
"type": "boolean",
"title": "Created By AI Agent",
"description": "Determines whether or not the PR was created by an AI agent such as Copilot, Claude, or Devin"
} -
Click
Saveto update the blueprint.
Update the Jira issue blueprint
To correlate AI adoption with operational metrics like bug resolution and incident response time, we need to add properties to track issue categories and lead time.
-
Go to the Builder page of your portal.
-
Find the
jiraIssueblueprint and click on it. -
Click on the
{...}button in the top right corner, and chooseEdit JSON. -
Add the following properties to the
propertiessection:Issue category and lead time properties (click to expand)
"issue_category": {
"title": "Issue Category",
"type": "string",
"enum": ["Bug", "Security Issues", "Incidents", "Other"],
"enumColors": {
"Bug": "red",
"Security Issues": "orange",
"Incidents": "pink",
"Other": "lightGray"
},
"description": "Category of the issue for tracking purposes"
},
"lead_time_hours": {
"title": "Lead Time (Hours)",
"type": "number",
"description": "Time from issue creation to resolution in hours"
} -
Click
Saveto update the blueprint.
Update integration mapping
Now we'll configure the GitHub integration to detect AI-assisted PRs and Jira issues to populate the issue category and lead time properties.
Github Integration mapping
-
Go to your Data Source page.
-
Select the GitHub integration.
-
Add or update the following YAML block in the editor:
GitHub integration configuration (click to expand)
resources:
- kind: repository
selector:
query: 'true'
teams: true
port:
entity:
mappings:
identifier: .full_name
title: .name
blueprint: '"githubRepository"'
properties:
readme: file://README.md
url: .html_url
defaultBranch: .default_branch
last_push: .pushed_at
visibility: .visibility
language: .language
- kind: pull-request
selector:
query: 'true'
closedPullRequests: true
port:
entity:
mappings:
identifier: .id|tostring
title: .title
blueprint: '"githubPullRequest"'
properties:
status: .status
closedAt: .closed_at
updatedAt: .updated_at
mergedAt: .merged_at
createdAt: .created_at
link: .html_url
created_by_agent: .user.login | ascii_downcase | test("(copilot|claude|devin)")
leadTimeHours: >-
(.created_at as $createdAt | .merged_at as $mergedAt | ($createdAt
| sub("\\..*Z$"; "Z") | strptime("%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%SZ") | mktime)
as $createdTimestamp | ($mergedAt | if . == null then null else
sub("\\..*Z$"; "Z") | strptime("%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%SZ") | mktime end)
as $mergedTimestamp | if $mergedTimestamp == null then null else
(((($mergedTimestamp - $createdTimestamp) / 3600) * 100 | floor) /
100) end)
pr_age: >-
((now - (.created_at | sub("\\.[0-9]+Z$"; "Z") | fromdateiso8601))
/ 86400) | round
cycle_time: >-
if .merged_at then (((.merged_at | sub("\\.[0-9]+Z$"; "Z") |
fromdateiso8601) - (.created_at | sub("\\.[0-9]+Z$"; "Z") |
fromdateiso8601)) / 86400 | round) else null end
relations:
repository: .head.repo.full_nameAI agent detectionThe mapping uses a regex pattern to detect AI agents by checking if the PR creator's username contains "copilot", "claude", or "devin" (case-insensitive). You can customize this pattern to match your organization's AI agent naming conventions.
-
Click
Save & Resyncto apply the mapping.
Configure Jira integration mapping
-
Go to your Data Source page.
-
Select the Jira integration.
-
Update the
jiraIssuemapping to include the new properties:Jira integration mapping for issue properties (click to expand)
- kind: issue
selector:
query: 'true'
port:
entity:
mappings:
identifier: .key
title: .fields.summary
blueprint: '"jiraIssue"'
properties:
# ... existing properties ...
issue_category: |
if .fields.labels | any(. == "security") then "Security Issues"
elif .fields.issuetype.name == "Bug" then "Bug"
elif .fields.issuetype.name == "Incident" then "Incidents"
else "Other" end
lead_time_hours: |
if .fields.resolutiondate != null then
((.fields.resolutiondate | fromdateiso8601) - (.fields.created | fromdateiso8601)) / 3600 | round
else
null
endIssue category logicThe mapping categorizes issues based on labels and issue type. Issues with a "security" label are classified as Security Issues, Bug types as Bug, and Incident types as Incidents. You can customize this logic to match your organization's issue classification.
-
Click
Save & Resyncto apply the mapping.
Visualize metrics
Once the data is synced, we can create a dedicated dashboard in Port to monitor and analyze AI adoption and impact metrics.
Create a dashboard
- Navigate to your software catalog.
- Click on the
+ Newbutton in the left sidebar. - Select New dashboard.
- Name the dashboard AI Adoption and Impact.
- Click
Create.
We now have a blank dashboard where we can start adding widgets to visualize AI adoption metrics.
Add widgets
In the new dashboard, create the following widgets. Some widgets are specific to your chosen AI tool, while others work with any tool.
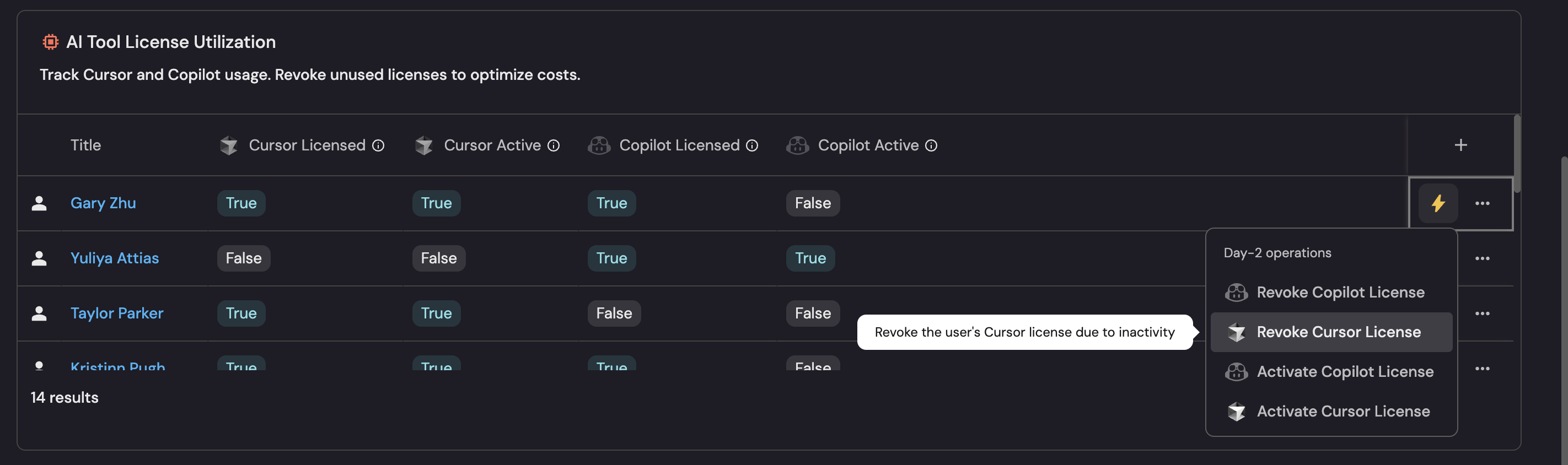
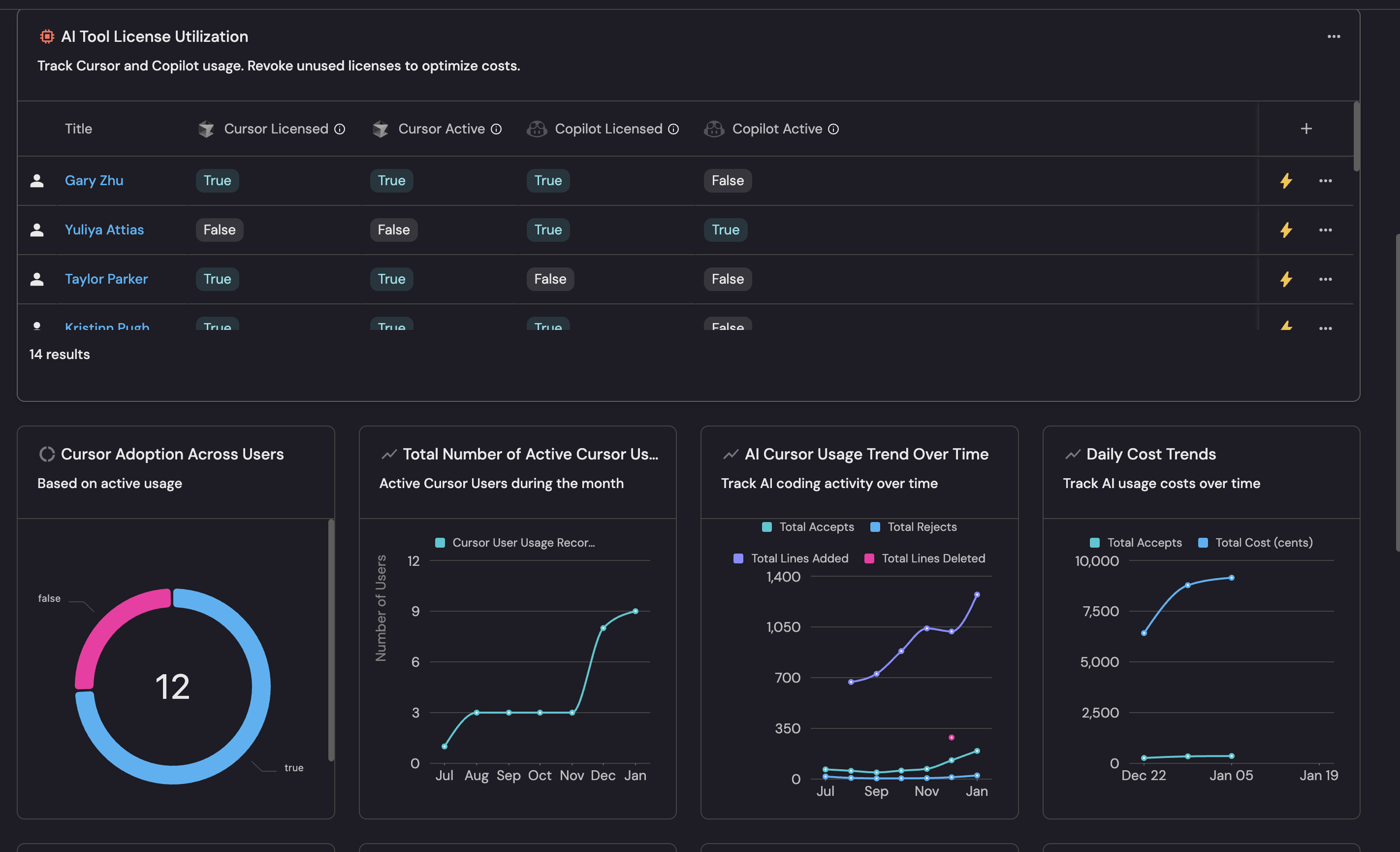
AI Tool License Utilization table (click to expand)
This table shows all users with their AI tool license and usage status across both Cursor and Copilot, allowing you to identify unused licenses for cost optimization.
- Click
+ Widgetand select Table. - Title:
AI Tool License Utilization. - Description:
Track Cursor and Copilot usage. Revoke unused licenses to optimize costs. - Choose the User blueprint.
- Click Save to add the widget to the dashboard.
- Click on the
...button in the top right corner of the table and select Customize table. - In the top right corner of the table, click on
Manage Propertiesand add the following columns:- Title: User's name.
- Cursor Licensed: Whether user has a Cursor license.
- Cursor Active: Whether user has used Cursor in last 90 days.
- Copilot Licensed: Whether user has a Copilot license.
- Copilot Active: Whether user has used Copilot in last 90 days.
- Click on the save icon in the top right corner of the widget to save the customized table.
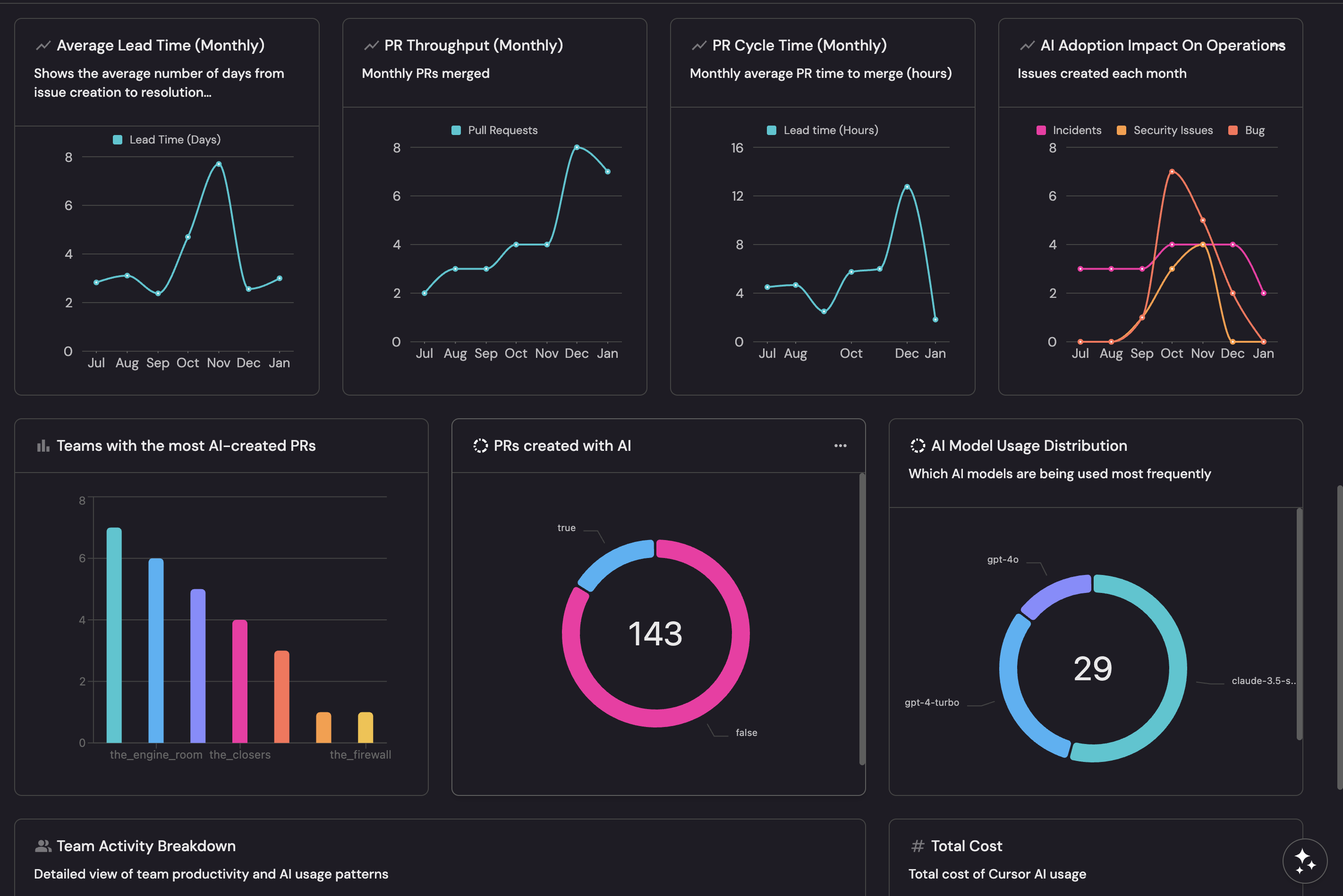
Average Lead Time (Monthly) line chart (click to expand)
-
Click
+ Widgetand select Line Chart. -
Title:
Average Lead Time (Monthly). -
Description:
Shows the average number of days from issue creation to resolution. -
Select
Aggregate Property (All Entities)Chart type and choose Pull Request as the Blueprint. -
Select
leadTimeHoursas the Property. -
Select
averagefor the Function. -
Input
Lead Time (Days)as the Y axis Title. -
Input
Dateas the X axis Title. -
Select
createdAtfor Measure time by. -
Set Time Interval to
monthand Time Range toIn the past 6 months. -
Add this JSON to the Additional filters editor:
{
"combinator": "and",
"rules": [
{
"value": "merged",
"property": "status",
"operator": "="
}
]
} -
Click
Save.
PR Throughput (Monthly) line chart (click to expand)
-
Click
+ Widgetand select Line Chart. -
Title:
PR Throughput (Monthly). -
Description:
Monthly PRs merged. -
Select
Count Entities (All Entities)Chart type and choose Pull Request as the Blueprint. -
Select
countfor the Function. -
Input
Pull Requestsas the Y axis Title. -
Input
Dateas the X axis Title. -
Select
createdAtfor Measure time by. -
Set Time Interval to
monthand Time Range toIn the past 6 months. -
Add this JSON to the Additional filters editor:
{
"combinator": "and",
"rules": [
{
"value": "merged",
"property": "status",
"operator": "="
}
]
} -
Click
Save.
PR Cycle Time (Monthly) line chart (click to expand)
-
Click
+ Widgetand select Line Chart. -
Title:
PR Cycle Time (Monthly). -
Description:
Monthly average PR time to merge (hours). -
Select
Aggregate Property (All Entities)Chart type and choose Pull Request as the Blueprint. -
Select
cycle_timeas the Property. -
Select
averagefor the Function. -
Input
Lead time (Hours)as the Y axis Title. -
Input
Dateas the X axis Title. -
Select
createdAtfor Measure time by. -
Set Time Interval to
monthand Time Range toIn the past 6 months. -
Add this JSON to the Additional filters editor:
{
"combinator": "and",
"rules": [
{
"value": "merged",
"property": "status",
"operator": "="
}
]
} -
Click
Save.
PRs created with AI pie chart (click to expand)
- Click
+ Widgetand select Pie chart. - Title:
PRs Created with AI. - Choose the Pull Request blueprint.
- Under
Breakdown by property, select the Created By AI Agent property. - Click Save.
Teams with the most AI-created PRs bar chart (click to expand)
-
Click
+ Widgetand select Bar Chart. -
Title:
Teams with the most AI-created PRs. -
Choose the Pull Request blueprint.
-
Under
Breakdown by property, select the Owning Team property (via repository relation). -
Add this JSON to the Additional filters editor:
{
"combinator": "and",
"rules": [
{
"value": true,
"property": "created_by_agent",
"operator": "="
}
]
} -
Click Save.
AI Adoption Impact On Operations line chart (click to expand)
This chart shows the monthly trend of bugs, security issues, and incidents to help correlate AI adoption with operational quality.
-
Click
+ Widgetand select Line Chart. -
Title:
AI Adoption Impact On Operations. -
Description:
Issues created each month. -
Select
Count Entities (All Entities)Chart type and choose Jira Issue as the Blueprint. -
Under
Breakdown by property, select the Issue Category property. -
Input
Issuesas the Y axis Title. -
Input
Dateas the X axis Title. -
Select
createdAtfor Measure time by. -
Set Time Interval to
monthand Time Range toIn the past 6 months. -
Add this JSON to the Additional filters editor to only show relevant categories:
{
"combinator": "and",
"rules": [
{
"property": "issue_category",
"operator": "in",
"value": ["Bug", "Security Issues", "Incidents"]
}
]
} -
Click
Save.
Set up self-service actions (optional)
You can set up self-service actions to activate or revoke AI tool licenses. These actions allows you to easily activate or revoke licenses for users in your organization directly from your Port dashboard.
- Cursor
- GitHub Copilot
Activate Cursor License action (click to expand)
This action calls the Cursor API to add a user to your team, which provisions their license.
-
Go to the Self-service page of your portal.
-
Click on
+ Action. -
Select the User blueprint.
-
Copy and paste the following JSON schema:
{
"identifier": "activate_cursor_license",
"title": "Activate Cursor License",
"icon": "Cursor",
"description": "Activate a Cursor license for this user",
"trigger": {
"type": "self-service",
"operation": "DAY-2",
"userInputs": {
"properties": {
"confirm": {
"type": "boolean",
"title": "Confirm Activation",
"description": "Check this box to confirm you want to activate a Cursor license"
}
},
"required": ["confirm"]
}
},
"invocationMethod": {
"type": "WEBHOOK",
"url": "https://api.cursor.com/teams/members",
"agent": false,
"synchronized": true,
"method": "POST",
"headers": {
"Authorization": "Bearer {{ .secrets.CURSOR_API_KEY }}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
"body": {
"email": "{{ .entity.properties.email }}"
}
}
} -
Click
Createto save the action. -
Add your Cursor API key as a secret named
CURSOR_API_KEYin your Port secrets.
Revoke Cursor License action (click to expand)
This action calls the Cursor API to remove a user from your team, which revokes their license.
-
Go to the Self-service page of your portal.
-
Click on
+ Action. -
Select the User blueprint.
-
Copy and paste the following JSON schema:
{
"identifier": "revoke_cursor_license",
"title": "Revoke Cursor License",
"icon": "Cursor",
"description": "Revoke the Cursor license for this user",
"trigger": {
"type": "self-service",
"operation": "DAY-2",
"userInputs": {
"properties": {
"confirm": {
"type": "boolean",
"title": "Confirm Revocation",
"description": "Check this box to confirm you want to revoke the Cursor license"
}
},
"required": ["confirm"]
}
},
"invocationMethod": {
"type": "WEBHOOK",
"url": "https://api.cursor.com/teams/members/{{ .entity.properties.email }}",
"agent": false,
"synchronized": true,
"method": "DELETE",
"headers": {
"Authorization": "Bearer {{ .secrets.CURSOR_API_KEY }}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
}
} -
Click
Createto save the action. -
Add your Cursor API key as a secret named
CURSOR_API_KEYin your Port secrets.
The Cursor API endpoint DELETE /teams/members/{email} removes a user from your Cursor team. Refer to the Cursor API documentation for more details.
Activate Copilot License action (click to expand)
This action calls the GitHub API to add a user to the Copilot subscription.
-
Go to the Self-service page of your portal.
-
Click on
+ Action. -
Select the User blueprint.
-
Copy and paste the following JSON schema:
{
"identifier": "activate_copilot_license",
"title": "Activate Copilot License",
"icon": "Github",
"description": "Activate a GitHub Copilot license for this user",
"trigger": {
"type": "self-service",
"operation": "DAY-2",
"userInputs": {
"properties": {
"confirm": {
"type": "boolean",
"title": "Confirm Activation",
"description": "Check this box to confirm you want to activate a Copilot license"
}
},
"required": ["confirm"]
}
},
"invocationMethod": {
"type": "WEBHOOK",
"url": "https://api.github.com/orgs/YOUR_ORG/copilot/billing/selected_users",
"agent": false,
"synchronized": true,
"method": "POST",
"headers": {
"Authorization": "Bearer {{ .secrets.GITHUB_COPILOT_ADMIN_TOKEN }}",
"Accept": "application/vnd.github+json",
"X-GitHub-Api-Version": "2022-11-28"
},
"body": {
"selected_usernames": ["{{ .entity.properties.github_username }}"]
}
}
} -
Replace
YOUR_ORGwith your GitHub organization name. -
Click
Createto save the action. -
Add your GitHub token as a secret named
GITHUB_COPILOT_ADMIN_TOKENin your Port secrets. The token requires themanage_billing:copilotscope.
Revoke Copilot License action (click to expand)
This action calls the GitHub API to remove a user's Copilot license assignment.
-
Go to the Self-service page of your portal.
-
Click on
+ Action. -
Select the User blueprint.
-
Copy and paste the following JSON schema:
{
"identifier": "revoke_copilot_license",
"title": "Revoke Copilot License",
"icon": "Github",
"description": "Revoke the GitHub Copilot license for this user",
"trigger": {
"type": "self-service",
"operation": "DAY-2",
"userInputs": {
"properties": {
"confirm": {
"type": "boolean",
"title": "Confirm Revocation",
"description": "Check this box to confirm you want to revoke the Copilot license"
}
},
"required": ["confirm"]
}
},
"invocationMethod": {
"type": "WEBHOOK",
"url": "https://api.github.com/orgs/YOUR_ORG/copilot/billing/selected_users",
"agent": false,
"synchronized": true,
"method": "DELETE",
"headers": {
"Authorization": "Bearer {{ .secrets.GITHUB_COPILOT_ADMIN_TOKEN }}",
"Accept": "application/vnd.github+json",
"X-GitHub-Api-Version": "2022-11-28"
},
"body": {
"selected_usernames": ["{{ .entity.properties.github_username }}"]
}
}
} -
Replace
YOUR_ORGwith your GitHub organization name. -
Click
Createto save the action. -
Add your GitHub token as a secret named
GITHUB_COPILOT_ADMIN_TOKENin your Port secrets. The token requires themanage_billing:copilotscope.
The GitHub API endpoint DELETE /orgs/{org}/copilot/billing/selected_users removes Copilot access for specified users. Refer to the GitHub Copilot API documentation for more details.